Theme:
Pediatrics Conference 2020
With the co-ordination of our honourable editorial board committee and congress organizing committee, we are privileged to welcome Paediatricians, neonatologists, infectious disease specialists, pulmonologist, microbiologist, Nutritionist, Child care specialists, Doctors, Nurses, pharmacologists, physicians, Healthcare specialists, students, Young research fellows, students, Professors, academicians etc. to our upcoming virtual conference “2nd International Paediatrics, Infectious Diseases and Healthcare Conference”, scheduled on October 26-27, 2020 (Dubai Time Zone).
Register Now
Webinar Objectives:
- Nanotechnology in Paediatric Infectious Diseases
- Paediatric Pharmacology
- Perinatal HIV and Breast Feeding
- Paediatric Healthcare and Nutrition
- Onco-pedic Effects and Approaches
- Challenging Tropical Diseases in Children
- Paediatric Metabolic Disorder- Recent Epidemics
- Recent Advances in Paediatric Interventional Cardiology
- Neonatal and Congenital Infections
- Paediatric Nursing and Surgery
The board committee are privileged to welcome experienced professionals, young research fellows, students to present their research virtually and to get their research published in our supporting journals. Both abstracts and full length paper are accepted for the publication purpose in our conference supporting journals.
Mostly students and young researchers are requested to submit their researches via posters, which will undergo detailed review process for the acceptance and selected abstracts will be proceeded for publication and further proceedings.
- Access to All Sessions Online
- E-Handbook & E-Conference Kit
- E-Certificate of Presentation
- Online publication of Abstract and Biography in our website which has 25 Million visitors
- Online publication of Abstract and Biography in respective conference webpage which has 25,000 online unique subject experts’ visitors
For more info:
Email: pediatrichealth@globalconferencemeet.com
Whatsapp: +447723584478
Track 1: Pediatrics
Pediatrics is the field of medicine that is concerned about the well-being of neonatal, children, and adults. It also concerns on their development and advancement and their chance to accomplish maximum capacity as grown-ups. The Pediatric academy of America, prescribes that the children should be under pediatric care, up to the age of 21. The point of investigation of pediatrics is to decline the death rate of children and newborns, to control the spread of infectious diseases, for a long ailment free life.
Track 2: Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases, which annually claim about 14 million lives i.e. 25% of the more or less 56 million deaths recorded worldwide. The recent trends of pediatrics have achieved exceptional advances in reductions in childhood mortality. The global challenge of preventing HBV in children has shown that the deadliest infectious diseases can be prevented by acquiring proper awareness.
Track 3: Nanotechnology in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
One of the emerging technologies recently is, Nanotechnology. The stream is very effective because it aims with target drug delivery. Nanotechnology is the manipulation of material on an atomic and molecular scale, by changing its physical, chemical and biological properties to produce novel materials, devices, and systems. Immunological techniques use nanotechnology to improve the health of the patients because of its biocompatibility. Nanoparticles can have cytotoxic, genotoxic, and inflammatory effects in mammalian cells, and can induce oxidative stress response, which should be considered before selection of Nano technological approach. The most important things are,
- High surface area
- Intrinsic toxicity
Recent study suggests that iron oxide nanoparticles were found in large variety of organism and they have collected response due to their super paramagnetic properties. The current study suggests that biofilm associated diseases are difficult to treat and hence the field of medicine uses Nanomaterial and Nanostructure.
Track 4: Pediatric Pharmacology
Age-adapted drug formulations are a challenge in drug development. In formulating medications for pediatric, manufacturers must concentrate on dysphagia, dosing and physiological changes. The fact is that many of the pediatric medicines are scaled-down geriatric medicines. In infants and adults, the immaturity of the enzyme may determine the pharmacokinetics of the excipients. A study suggests that wrong medications might lead to adverse drug effects. A survey shows that hospitalization due to adverse effects is 4times higher in infants when compared with adults.
Track 5: Perinatal HIV and Breast Feeding
This section intends to provide potential risk associated with breast feeding in HIV infected women. Mothers infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) can transmit the virus to their babies in utero, intrapartum or postpartum through breastfeeding. With response to community, edits were continued to integrate people’s language which focuses on person, rather than the diseases, says the survey. Mother-to-child HIV transmission reported that 2.1 million children living with HIV and 430,000 new HIV infections in infants occurring every year due to breast feeding. Hence efforts were made by making breastfeeding safer by using antiretroviral prophylaxis to either mothers or their infants.
Advances were made in the field of perinatal HIV by providing an elvitegravir/cobicistat regimen as a therapeutic drug in deducing the viral load and therapeutics like intrapartum intravenous (IV) zidovudine as it is very effective in reducing the risk of transmission of HIV, the recent trend suggests that, a single dose of oral nevirapine to mothers during labor and to neonates would further reduce transmission of HIV.
Track 6: Pediatric Healthcare and Nutrition
The world of nutrition and healthcare is constantly changing, as new technologies emerge. Nutritional requirements differ for children when compared with adults, as they are in their growing age they need balanced nutrition. In the prenatal period, infant’s growth totally depends on maternal nutrition. They need for calories, especially in the form of protein, are greater than at any postnatal period because of rapid increase in both height and weight. Breastfeeding to age 2 years with appropriate complementary feeding after 6 months contributes to good nutrition, a study suggests.
The trends in nutrition recommended Paleo diet for children as it is rich in high-protein, high-fiber diet consisting of lean meat, fish, fruits, veggies, eggs and oil and it is a gluten free diet. Since pediatric nutrition concerns the mother, the pediatric nutrition market is emerging globally at a significant pace.
Track 7: Onco-pedic Effects and Approaches
With the increased population of children diagnosed with cancer, technology makes changes in pediatric oncology nursing care, treatment and prognosis. The incidence of cancer in childhood is increasing abruptly. It is estimated that the incidence of childhood cancer is increasing by 0.6% per year.
Advances in the treatment of childhood cancer have shown an improvement in prognosis in recent years. Therefore, survivor rate of children with cancer is going to rise in the past decade. The recent trends in the treatment of pediatric oncology say that radiolabeled 131-I-MIBG selectively targets radiation to catecholamine-producing Neuroblastoma cells. Monoclonal antibodies play a vital role in the treatment of cancer in the field of onco-ped. They are designed to potentiate chemotherapy, particularly in the setting of relapsed leukaemia. Four out of five children diagnosed with cancer can be cured with contemporary cancer therapy. Only a small percentage of childhood cancers, are due to familial or genetic factors and an even smaller percentage of childhood cancer has an identified environmental link.
Track 8: Obesogenic Factors and Recent Innovations
According to public health England, quarter of children between the age group of 2 – 10 years old are overweight or obese around the globe and by 2034, 70 per cent of adults are expected to be obese. Children who are obese are at greater risk for high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes and heart disease and the study also suggests that Obesity rates are higher among Blacks and Latinos than among Whites and Asian Americans. The recent innovations in pediatric obesity says that Percent overweight (%OW) is helpful for providing evidence of weight change in severely obese children and recent treatment involves Lifestyle intervention which modifies children’s daily dietary and activity behaviors, targeting sustainable changes associated with healthy weight management. Pharmacotherapy is an emerging trend in the treatment of obesity in children but facing with side effects is the only cons it has.
Track 9: Challenging Tropical Diseases in Children
The Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) of around 17 or more parasitic diseases and its related infections represent the most common illness. Population growth, urbanization, deficiencies in water and sanitation systems lead to re- emergence of tropical diseases says the study. Cases of Neuro-schistosomiasis, Neurocysticercosis, and Chagasic stroke are increasingly detected in western countries. Recently, Chikungunya virus adapted to Aedus albopictus is spread in Europe has been reported. Dengue fever is the second most common mosquito-borne disease after malaria, and every year more than 50 million cases of dengue fever resulting in 25,000 fatalities.
The pipelines for new drugs for these diseases have been dried for the past 3decades due to the absence of commercial market. Recently, Metallo-β-lactamase has been isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae, offering few treatment opportunities. Several vaccines, including vaccines against hookworm infection, schistosomiasis and leishmaniasis are in phase 1 and phase 2 clinical trials for product development. These would be used as “vaccine-linked chemotherapy” alongside drugs in a comprehensive treatment.
Track 10: Pediatric Metabolic Disorder- Recent Epidemics
Metabolism is carried out by chemical substances called enzymes, which are made by cells in the body. If a genetic abnormality affects the function of an enzyme or causes it to be deficient or missing altogether, various metabolic disorders can occur. Metabolic disorders are classified by the particular building block that is affected. These disorders usually result from an,
- Inability to break down a substance that should be broken down, allowing a toxic intermediate substance to build up
- Inability to produce some essential substance
The recent epidemics of metabolic diseases cannot be attributed only to genetic background and changes in diet, exercise and aging. Metabolic diseases have their origins during development due to altered programming that increases susceptibility to disease later in life. Metabolism disruptors are endocrine disruptors that increase the susceptibility to metabolic diseases. Some metabolism disruptors may cause metabolic diseases pursue while others act via increasing the sensitivity or set point for disease. The metabolic disruptor hypothesis provides a focus on preventing metabolic diseases.
Track 11: Recent Advances in Pediatric Interventional Cardiology
For the past 10 years, there have been vast technological achievements in Pediatric interventional cardiology. In addition to that, there have been several advances in cardiac imaging, especially in 3-dimensional imaging of echocardiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and cine-angiography. Some advancement that reflect mainly on adult population, such as patent foramen ovale device closure and closure of post infarct ventricular septal defects aimed solution for Pediatric Cardiology. Therefore, more types of congenital heart diseases can be treated in the cardiac catheter laboratory today than ever before. As a result of recent technological advances, more types of CHDs than ever before are now possible to treat in the cardiac catheter laboratory. Furthermore, lesions previously considered resistant to interventional therapies can now be managed with high success rates. However, most current recommendations for interventional procedures refer to off-label use of devices. Nevertheless, the Pediatric interventional cardiology community has made attempts to develop better solutions to minimize the need for open heart surgery and optimize overall outcomes.
Track 12: Fungal and Bacterial Infections: Head to Toe
Children are prone to various infections. No matter how clean the environment is, the inherent nature of germs, tend to attract bacteria and other microbes. When babies are born, they come with a completely sterile digestive system and the immune system has not been activated. By preventing fungal infections, we ensure child’s wellbeing. The prevalence of fungal and bacterial infections is increasing, representing an enormous challenge to healthcare professionals. This increase is directly related to the growing population of immunocompromised individuals especially children with the use of intensive chemotherapy and immunosuppressive drugs.
Bacteria have been recognized as a cause of serious infection with increased frequency during the past 2 decades. Virtually not all fungi are pathogenic, and their infection is opportunistic. Opportunistic fungal infections cause diseases exclusively in immune-compromised individuals. Recent study has been reported that, the fungal infections in babies and infants, if left untreated, are dangerous and can even lead to death due to compromised immune systems and weakening inflammatory response. The current trend in treating bacterial and fungal infection is Soy, a hormone disruptor. About 75% of the U.S. soy crop is now genetically engineered.
Track 13: Neonatal and Congenital Infections
Newborn congenital infections have a variety of causes fluctuate from pregnancy to genetic malformations in utero. In many cases, however, a congenital anomaly may have no known cause. For e.g. the structural defect such as spina bifida is obvious at birth, whereas hemophilia a functional defect (a bleeding disorder) is not usually obvious until infancy or childhood. An estimation of about 270 000 deaths during the first 28 days of life were reported due to congenital anomalies globally.
Advanced interventions of the neonatal infection risk have further led to identification of several promising potential biomarkers that may translate to improved diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of neonatal sepsis in the future. Very low birth weight is an important factor for neonatal infection. Microbial agents can be transmitted from the mother to the fetus either Trans placentally, haematogenously, or via the birth canal. Microbial agents may penetrate the placental barrier and contaminate the fetus, often leading with neonatal infections. Recent studies revealed that emerging pathogens are predominantly Gram positive, of which coagulase-negative staphylococci are the commonest organisms accounting for 45–75% of all late-onset bloodstream infections.
Track 14: Pediatric Nursing and Surgery
The Advanced Practice Nurse (APN) functions in pediatric surgery in a variety of ways. Changes in the standard of care for pediatric patients are not something the medical community takes lightly. However, there is an exception when developing clinical care guidelines for use with the pediatric patient. The recent interventions in the field of pediatric nursing paves way for the use of a machine to take over the work of the lungs, and sometimes the heart, as a rescue therapy—has given patients a second chance at life over the last 25 years and smart pills include a tiny sensor, when ingested, transmit a signal to a patch the patient wears.
The greatest intervention in the field of pediatric surgery is that the stem cells-have the potential to turn into anything—a skin cell, a liver cell, a brain cell. And stem cell transplants have the power to treat a wide range of diseases in children, from cancers like Leukemia, Lymphoma and Neuroblastoma to blood disorders, immune system diseases and bone marrow syndromes. The recent trends have reported that the chemical named sildenafil citric (the same chemical as Viagra) to reverse pulmonary hypertension.
Track 15: Healthcare Intervention- Pediatric Yoga Therapy
Yoga is a mind-body practice that originated in India at least 2000 years ago. It is recognized by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Centre for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) as a form of CAM in the category of “mind-body” medicine. NCCAM asserts that mind-body medicine focuses on the interactions among the brain, mind, body, and behaviour, and on the powerful ways in which emotional, mental, social, spiritual, and behavioural factors can directly affect health.
Thirty four controlled studies were identified published from 1979 to 2008, with 19 RCTS and 15 NRCTs. Clinical areas for which yoga has been studied include physical fitness, cardio-respiratory effects, motor skills/strength, mental health and psychological disorders, behaviour and development, irritable bowel syndrome, and birth outcomes following prenatal yoga. There is also a progressive trend toward use of yoga as a mind-body complementary and alternative medicine intervention to improve specific physical and mental health conditions. To provide clinicians with therapeutically useful information about yoga, the evidence evaluating yoga as an effective intervention for children with health problems is reviewed. Yoga appears promising as a complementary therapy for children.
Pediatrics, Infectious Diseases and Healthcare is nonpareil and open platform to explore and gain the knowledge in the field of Medical Science. This conference brings together Pediatricians, Microbiologists, Pathologists, Obstetricians, Immunologists, Neonatologists, Bacteriologists, Virologists, Professors, Oncologists, Nutrionists, Researchers, Scientists, Students in all the areas of Medical sciences, Pharmaceutical, Life sciences, Medical associations and societies, to enable an international forum to explore the approved research. ConferenceSeries Ltd is delight to invite you all to attend and register for the “2nd International Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Healthcare Conference” scheduled for October 26-27, 2020 at Cape Town, South Africa.
The Organizing Committee is gearing up for an exciting and factual conference program which includes plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs all over the world. We invite you to join us at the 2nd International Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Healthcare Conference 2020, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the 2nd International Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Healthcare Conference organizing committee look forward to meet you at Cape Town, South Africa.
Scope and Importance:
Pediatrics, Infectious Diseases and Healthcare 2020, deals exclusively with the Infectious Diseases, Interventions, Treatment and Healthcare involving children. It may be surprising for the lay public and even medical fraternity that the emerging disease, its treatment and diagnosis is now getting strenuous. About 8 new-born, out of one thousand live births will have one form of infectious diseases or other, ranging from minor to very complex ones. This would automatically entail fairly bulky health care burden. However it is a paradox that even the best educated are tuned to recognizing the existence of maladies as those afflicting predominantly the pediatric population. Both the public and private hospitals are readily catering to pediatric diseases, which albeit being very justifiable sometimes borders on to lucrative economic equations. Though Pediatric infectious diseases and healthcare 2020 has been one of the first outbreaks to be evolved in pediatrics, it aims at various informative and fruitful things to be delivered to the participants.
Pediatricians are expected to grow from nearly $23.8 billion in 2018 to roughly $55.1 billion by 2021, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.3% for the period of 2018-2021.
The average yearly salary for Pediatricians in South Africa is $28,243 USD. As it pertains to men v/s women, 1.5% of Pediatricians are females and 5.6% of pediatricians are males in South Africa.
Why Cape Town, South Africa?
Cape Town is a port city on South Africa’s southwest coast, on a peninsula beneath the Imposing Table Mountain. Slowly rotating cable cars climb to the mountain’s flat top, from which there are sweeping views of the city, the busy harbor and boats heading for Robben Island, the notorious prison that once held Nelson Mandela, which is now a living museum. The city is famous for its harbor for its natural setting in the Cape Floristic Region, and for such well-known landmarks as Table Mountain and Cape Point.
Cape Town has many blissful Research Institutes and Medical Centers for the welfare of the being. Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine (IDM) at UCT Faculty of Health Sciences, Cape Town, acknowledges strength and clinical aspects of infectious diseases research in the faculty of Health sciences.
Infectious Disease Research Institute (IDRI), South Africa and was established in 1994 as a not-for-profit US scientific organization to develop vaccines, therapeutics and diagnostics for a range of diseases of the developing world.
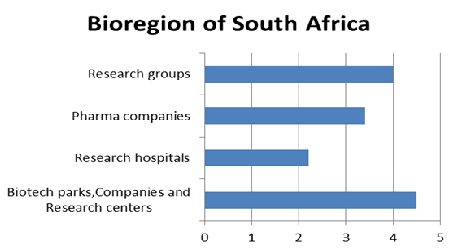
African Health’s vision is one of the organizations for the eradication of disease through early & innovative diagnostic techniques. A strong antimalarial drug candidate, progressive policies on genetically-modified crops, and a productive national research and development center are few things which make South Africa proud of it.
Global Market Analysis:
Young children need appropriate childcare and stimulation to thrive. Research has shown that quality protection, stimulation and learning opportunities. Every single day many children are affected due to infectious diseases. This survey aims to give a descriptive summary of infants and children suffering from infectious diseases worldwide.
In recent years, decrease in global mortality and improvement in quality of life is the most significant progresses in children and infants. In the field of pediatric infectious diseases, remarkable advances have been achieved in terms of reduction of incidence of childhood infectious diseases and associated morbidity and mortality. This is especially true for vaccine-preventable diseases where immunization against measles etc. The global challenge of controlling HBV dissemination well illustrates how preventive measures could hinder the serious course of an infectious disease.
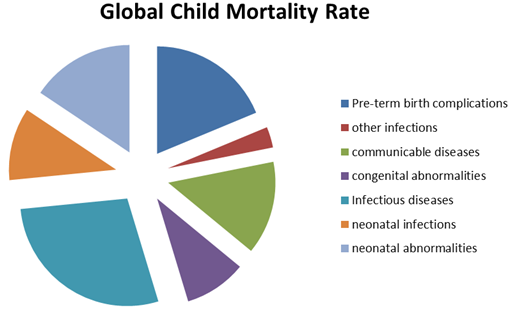
The old principle issued from Chinese traditional medicine “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” achieves its real significance when thinking about pediatric infectious disease. Again, the recent success story of preventing mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) well illustrates this keystone concept. In 1988, the HIV perinatal transmission rate around the world was 25%, and mortality in HIV-infected infants and children was high. The journal of infectious diseases society revealed a shocking data of that the hospitalized kids are inappropriately prescribed which results in 2.5% of global infant mortality.
Global Infection Rate:
Pneumonia accounted for approximately 16% of the 5.6 million under-five deaths, killing around 880,000 children in 2016. Most of its victims were less than 2 years old. Diarrhea is a leading killer of children, accounting for approximately over 1,300 young children dying each day, or about 480,000 children a year, despite the availability of simple effective treatment. Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the world’s deadliest diseases: One fourth of the world’s population is infected with TB. In 2016, 1.4 million children around the world became sick with TB disease.
Big countries like Brazil and China reduced their child mortality rates due to infectious diseases to 10-fold over the last 4 decades. Other countries – especially in Africa – still have high child mortality rates, but it’s not true that these countries are not making progress. In Sub-Saharan Africa, child mortality has been continuously falling for the last 50 years (1 in 4 children died in the early 60s – today it is less than 1 in 10).
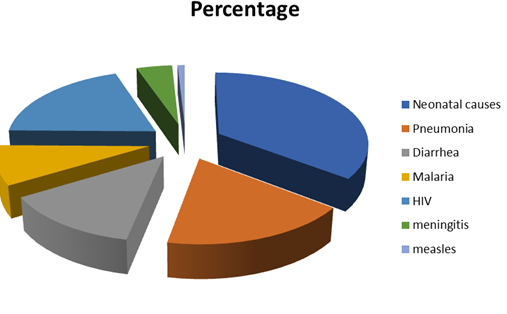
Over the last decade this improvement has been happening faster than ever before. Rising prosperity, rising education and the spread of health care around the globe are the major drivers of this progress. A media that would report global development could have had the headline “The number of children dying globally fell by 455 since yesterday” and they wouldn’t have this headline once but every single day over these more than 2 decades.
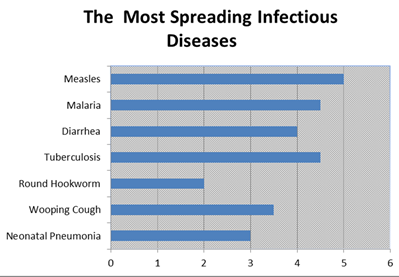
The most spreading infectious diseases are one of the first causes for the child maladies and mortalities. These diseases are in terms infectious and deadliest among children and infants if left untreated. Though vaccinations, treatments are available for these types of diseases, if not treated earlier causes death.
Market Analysis in South Africa:
Every baby, toddler and young child must be ensured the best start in life - their future, and indeed the future of their communities, nations and the whole world depends on it. With 5,164,500 children around the age group 0–4 years, South Africa has marked decline in poverty since 2000 and it is estimated that 55% of children live below the ultra-poverty line.
Children of age group 0-4 account for 10.4% of all deaths in South Africa. 40% of deaths in children under the age of five are caused by HIV-related illnesses. In South Africa, malnutrition in children is characterized by both under and over-nutrition, a direct reflection of the broader social disparities. Breastfeeding is a cultural norm in South Africa, but exclusive breastfeeding is not common.
According to the Demographics and Health Survey, mortality rates for children under the age of five show no significant change at national level. The infant mortality rate also registered a change, from 45 per 1,000 live births in 1998 to 58.5 per 1,000 live births in 2017. In 2005, children aged 0–4 accounted for 10.4% of all deaths in South Africa. HIV-related illnesses are the single greatest cause of death in children under five, accounting for 40% of deaths. 3.3% of South African children aged between 2-14 are living with HIV .There is a sharp decrease in prevalence in boys and girls aged 10–14, indicating that many children die in their early years. Without effective Prevention of Mother-to Child Transmission, 100,000 babies will contract HIV infection every year.
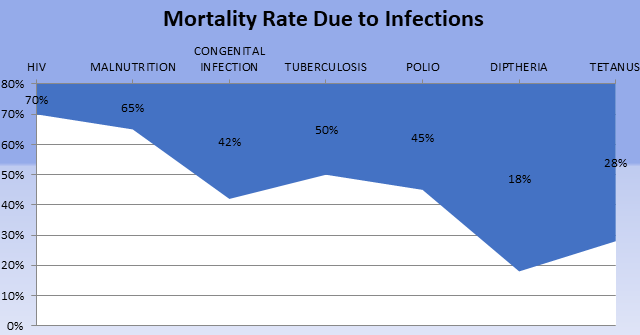
79% of children under the age of one are fully immunized against six deadly diseases but vaccine-preventable diseases: measles, tuberculosis, polio, diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis. These diseases are due to poor immune as these infants and children are not breastfeed as babies. Only 12 percent of children less than four months of age are exclusively breastfed. Supplementation of breastmilk starts early in South Africa. Most of the supplements are plain water or other liquids, increasing the risk of infection through contaminated liquids and the risk of malnutrition by feeding less nutrient-dense foods. This report reveals that young South African children are affected by a number of issues and trends. Neonatal mortality is also a concern.
Malnutrition in South Africa is characterized by both under and overnutrition, which reflects the broader social disparities. We definitively need new approaches to implement research and disseminate knowledge so that science and technological advances will be translated into policies easily available for people who need them the most.
Recent Outbreaks in Cape Town, South Africa:
Neonates who are hospitalized due to an emergency are prone to various other infections, with pathogen exposures occurring in utero, intrapartum, and postnatally. African neonatal units are at high risk of outbreaks due to overcrowding, poor-staffing, and due to an equipment sharing. The pediatric infectious diseases and infection prevention (IP) teams attended the neonatal outbreak unit at Tygerberg Children's Hospital, Cape Town.
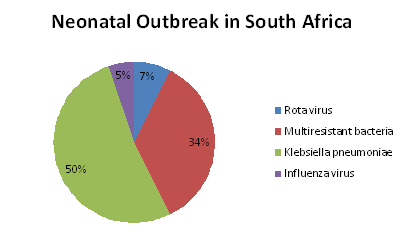
About 148 babies (7% mortality) over an 8-year period were documented, with pathogens including rotavirus, influenza virus, measles virus, and multidrug-resistant bacteria (Serratia marcescens, Acinetobacter baumannii, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and vancomycin-resistant enterococci). Although the infection source was rarely identified, most outbreaks were in vain. From the African neonatal literature, 20 outbreaks affecting about 524 babies (34% mortality) were identified; 50% of death was caused due to extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Thus, the current crisis in Neonates made a drastic outbreak globally. Hence, care for the Neonates should be revised and improved for the better way of living.
Universities and Colleges Related To the Conference
- U-Mass Memorial Medical Center
- University of Colorado
- Northwestern University
- University of Florida
- University of Oxford
- University at Buffalo
- Augusta University
- University of Missouri
- University of Toronto
- University of Arizona
- University of South Hampton
- Imperial College, London
- University of Utah health
- Stony Brook University of Medicine
- Medical University of South California
- Seoul National University of Infectious Diseases
- University of Rochester Medical Center
- Drexel University of Medicine
- Emory University of Medicine
- Swedish Institute for Infectious Diseases
- Upstate Medical University
- Vermont College of Medicine
- University of Gothenburg
- University of Otego
- Oslo University
- Queensland University of Technology
- University of Liverpool
- University of Colorado Denver
- Infectious Diseases Society of America
- Medical College of Georgia at Georgia Regents University
Hospitals Related to the Conference:
- Canada children’s and Women Hospital
- Phoenix children’s Hospital Foundation
- UC Davis children’s Hospital
- Sunrise Hospital and Medical Center
- St. Louis children’s Hospital
- Nelson Mandela’s children’s Hospital
- The Red Cross War Memorial Children’s Hospital
- KZN children’s Hospital
- Tygerberg Children’s Hospital
- Boston Children’s Hospital
- C.S Mott Children’s Hospital
- Randall Children's Hospital
- Children's Mercy Kansas City
- Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children
- Steven and Alexandra Cohen Children's Medical Center of New York
- Peyton Manning Children's Hospital
Tourists Attractions in Cape Town, South Africa
- Kirstenbosch
- Castle of good hope
- Cape Point
- Clifton Beach
- Bo-Kaap
- Victoria and Alfred Waterfront
- Boulders Beach Penguin Colony
- Robben Island
- Table Mountain
Associations and Societies
Pediatrics Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS), The Infectious Diseases Society Of America (IDSA), American Society Of Health System Pharmacists (ASHP), Making A Difference In Infectious Disease Pharmacotherapy (MAD-ID), National Foundation For Infectious Diseases (NFID), Society For Healthcare For Epidemiology Of America (SHEA), Society Of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP), American Academy of Pediatrics, American Pediatric Surgical Association, Mexican Board of Pediatric Surgery, OPEN Pediatrics Community European Society for Pediatric Research, American academy of Pediatrics Breastfeeding, American Childhood Cancer Organization, European Academy of Pediatrics, American Pediatric Surgical Nurses Association, European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, International Union Of Microbiological Societies, Federation Of Infection Societies, Canadian Society Of Microbiologists, British Infection Association, Infectious Diseases Society of America Global Pediatric Societies, Southern Society for Pediatric Research, Brooklyn pediatric society, European pediatric Association, International association of Pediatrics, Indian Academy of Pediatrics, Pediatric Associates of Savannah.
Bacterial infections often start with a mild infection in a children’s body, but gradually grows into a serious one which might be due to the neglection of parents and care takers of the child. Bacterial cells secrete toxins and harmful chemicals, which kill the immune cells by releasing surface structures called surface membrane vesicles containing toxins those target mitochondria of the host cells. Besides bacteria, some fungi too secrets toxins which directly damages host tissues and disable the immune system. Some of the most harmful bacterial toxins are Botulinum and Neurotoxins.
Some of the bacterial infections include:
- Strep throat
- Gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
- Syphilis
The rate of fungal infections in neonates are increasing rapidly, which have become a challenge for every healthcare professional to find out the unique and best treatments so as to minimize the rates and by guiding the care takers to learn the pediatric and neonatal cares professionally via online, training or any scientific discussions. For the pharmaceutical and biopharma sectors, these increasing rates of infection are creating a challenge to develop intensive chemotherapy and immunosuppressive drugs so as to scale up the production and capturing the market. Most of the pathogenic fungi occur I the form of Yeast, Mold and Dimorph. Sometimes, these infections increase high mortality and morbidity rate in the neonates.
Conference Highlights
- Pediatrics
- Nanotechnology in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
- Pediatrics Pharmacology
- Perinatal HIV and Breast Feeding
- Pediatric Healthcare and Nutrition
- Onco-pedic Effects and Approaches
- Obesogenic Factors and Recent Innovations
- Challenging Tropical Diseases in Children
- Pediatric Metabolic Disorder- Recent Epidemics
- Recent Advances in Pediatric Interventional Cardiology
- Fungal and Bacterial Infections: Head to Toe
- Healthcare Intervention- Pediatric Yoga Therapy
- Neonatal and Congenital Infections
- Pediatric Nursing and Surgery
- Infectious Diseases
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 26-27, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Health Education Research & Development
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Journal of AIDS & Clinical Research
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by